How to Handle Complex STEM Assignments: Data Tools & Analysis Guide
The transition from high school science to university-level STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) is often described by students as a “cliff.” In earlier years, academic success was largely about memorization—knowing the periodic table, understanding the basic laws of motion, or identifying biological structures. Tools like Quizlet are fantastic for this stage because they help cement definitions through repetition. However, as you move into higher education, the game changes entirely. You are no longer just expected to know what a concept is; you are expected to apply it to massive, messy datasets and communicate your findings through sophisticated visual models.
When you are staring at a spreadsheet with thousands of rows of raw data, the “cliff” can feel insurmountable. This is the point where many students experience burnout or a loss of confidence. The reality is that the smartest students aren’t necessarily the ones doing the most manual labor; they are the ones using the right tools to simplify the complex. If you find yourself hitting a wall during the data entry or interpretation phase, seeking professional Assignment Help from a reputable platform like myassignmenthelp can give you the structural roadmap needed to organize your thoughts and meet rigorous university standards. Utilizing such resources allows you to observe how experts bridge the gap between abstract numbers and professional-grade reports.
The Evolution of STEM Assignments in 2026
In the current academic landscape, the bar for “excellence” has been raised. Professors are no longer satisfied with a simple bar chart created in a basic spreadsheet. They are looking for “Data Literacy”—the ability to read, work with, analyze, and argue with data. Whether you are studying civil engineering, molecular biology, or data science, your assignments now require a multi-disciplinary approach. You need to be part mathematician, part coder, and part graphic designer.
The challenge is that most STEM programs teach you the theory but spend very little time teaching you the “art” of presentation. You might understand the physics of a bridge, but if you cannot visualize the stress points effectively in your report, your grades will suffer. This is why mastering data visualization tools is no longer an “optional” skill; it is a fundamental requirement for academic survival.
Understanding the Data Visualization Workflow
Before diving into specific software, it is vital to understand the process. Data visualization is not just about making things look “pretty.” It is about clarity. A successful STEM assignment follows a specific workflow that ensures the data remains the star of the show.
- Data Cleaning: Raw data is almost always “dirty.” There are missing values, typos, and outliers. Before you can visualize anything, you must prune the data.
- Selection of Variables: You cannot plot everything. You must decide which independent and dependent variables tell the most compelling story.
- Choosing the Right Narrative: Every graph should answer a question. Is there a correlation? Is there a trend over time? Is there a significant difference between two groups?
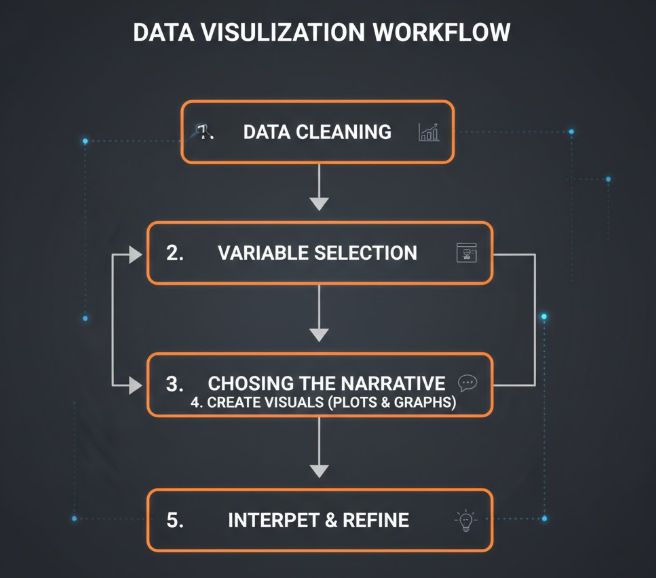
Interestingly, this process of selecting a narrative isn’t unique to science. It’s a form of critical analysis. For instance, when students explore various rhetorical analysis essay topics for their humanities electives, they are looking for the most persuasive way to present an argument. In STEM, your “rhetoric” is your data. You are using numbers and visuals to persuade your professor that your hypothesis is correct.
Top Tools for Data Visualization and Analysis
To handle the weight of modern STEM coursework, you need to move beyond the basics. Here are the tools that will give your assignments a professional edge:
1. Python: The Versatile Giant
Python has officially overtaken almost every other language in the academic world. Its popularity stems from its readability—it is often described as “coding in plain English.” For data visualization, Python offers two primary libraries:
- Matplotlib: Great for basic, high-quality 2D plots.
- Seaborn: Built on top of Matplotlib, it allows for more aesthetically pleasing and complex statistical graphics with fewer lines of code.
2. MATLAB: The Engineer’s Choice
If your degree has “Engineering” in the title, you will likely spend a lot of time in MATLAB. Unlike Python, which is general-purpose, MATLAB is specifically designed for matrix laboratory work. It is unparalleled when it comes to image processing, signal analysis, and complex mathematical modeling.
3. Tableau and Power BI
These are “Business Intelligence” tools, but they are increasingly used in environmental science and healthcare degrees. They allow you to create interactive dashboards. Imagine submitting a report where your professor can click a button on a map to see how different variables change in real-time. That is how you secure a top-tier grade.
Breaking Down Complex Analysis: A Step-by-Step Guide
To reach the 1400-word depth required for a comprehensive understanding of this topic, we must look at how to actually apply these tools to a real-world assignment scenario.
Step 1: The Hypothesis Phase
Every great STEM assignment begins with a question. “Does the temperature of a liquid affect the rate of chemical reaction?” or “How does urban density impact local air quality?” Before you touch any software, write down your expected outcome. This prevents “data fishing,” where you just look for any pattern without a purpose.
Step 2: Gathering and Importing Data
In 2026, data often comes from sensors, online databases (like Kaggle or government archives), or your own lab experiments. Learning how to import .csv or .json files into your chosen tool is your first technical hurdle.
Step 3: The “Visual Audit”
Once your data is in the tool, do a quick visual check. Use a “Scatter Plot” to see the distribution. Are there dots far away from the rest? These are outliers. You need to explain in your assignment why those outliers exist. Did the sensor malfunction? Or did something unexpected happen in the experiment? Professors love when you acknowledge “errors”—it shows you aren’t just faking the results.
Step 4: Refining the Aesthetics
A professional STEM assignment avoids “chart junk.” This means removing unnecessary grid lines, using color-blind friendly palettes, and ensuring all axes are labeled with correct units (e.g., Pressure in Pascals vs just Pressure).
Overcoming the “Writing Wall” in STEM
Even with the best graphs in the world, a STEM assignment is still a piece of writing. This is where many technical-minded students struggle. You have the data, you have the graphs, but how do you explain them?
The secret is to use the “Assertion-Evidence-Explanation” model:
- Assertion: State the trend shown in the graph. (e.g., “Figure 1 shows a direct correlation between X and Y.”)
- Evidence: Reference specific data points. (e.g., “As X increased by 10%, Y rose by an average of 15%.”)
- Explanation: Connect it back to the theory. (e.g., “This supports the Second Law of Thermodynamics because…”)
This structured approach ensures that your writing is as precise as your math. It removes the “fluff” and focuses on the logic, which is exactly what markers in the UK and global universities are looking for.
The Role of Collaborative Learning and Support
Sites like Quizlet Live have proven that we learn better when we collaborate. STEM shouldn’t be a lonely endeavor. Discussing your data with peers or seeking external feedback is a vital part of the scientific process. In the professional world, scientists “peer-review” each other’s work. In the student world, using academic support services or tutoring is your version of that peer-review. It’s about ensuring that your logic holds up under scrutiny before you submit the final version.
Why Students Struggle with STEM Visualization
The primary reason students fail to master these tools isn’t a lack of intelligence; it’s a lack of time. Between lectures, part-time jobs, and personal lives, finding twenty hours to learn Python from scratch is difficult.
This is why a “Hybrid Approach” to learning is best:
- Use AI and Tools for Drafts: Use software to generate the initial code or graphs.
- Use Professional Services for Structure: Learn from experts how to format and polish.
- Use Community Tools for Memorization: Use Quizlet to keep the core formulas fresh in your mind.
Conclusion: Mastering the Future of STEM
Handling complex STEM assignments is a journey of constant adaptation. The tools we use today—Python, MATLAB, and Tableau—might be replaced by even more advanced AI-driven platforms in the next five years. However, the fundamental skill of data visualization and analysis will remain the same.
To succeed, you must remain curious and be willing to step outside your comfort zone. Don’t be afraid of the code. Don’t be afraid to ask for help when the data becomes overwhelming. Whether you are seeking Assignment Help to get through a tough semester, or spending late nights debugging your own scripts, remember that every challenge is building your “technical muscle.”
By mastering these tools now, you aren’t just finishing an assignment; you are preparing for a career. The world is run by data, and those who can visualize that data are the ones who will lead the future of science and technology. Keep your graphs clear, your analysis deep, and your curiosity high—the rest will follow.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best way to start a complex data analysis project?
Begin by clearly defining your research question or hypothesis. Before touching any software, organize your raw data into a clean format (like a spreadsheet) to identify missing values or errors that could skew your final results.
Do I need to be a programmer to visualize STEM data?
While coding skills in Python or R offer the most flexibility, they aren’t strictly required. Many students successfully use “drag-and-drop” software or advanced graphing tools that provide professional-grade visuals without requiring deep programming knowledge.
How can I make my graphs look professional for university submissions?
Focus on clarity and simplicity. Ensure every axis is labeled with units, use high-contrast colors that are easy to read, and avoid unnecessary 3D effects or “chart junk” that might distract from the actual data trends.
What should I do if my data shows unexpected results or outliers?
Do not ignore or delete them. Instead, address them in your analysis. Explain potential reasons for the deviation—whether it was an experimental error or an interesting anomaly—as this demonstrates high-level critical thinking to your markers.
About The Author:
Alice Anderson is a dedicated academic researcher and contributing writer for myassignmenthelp, specializing in educational technology and student success strategies. With a passion for simplifying complex learning processes, alice focuses on bridging the gap between classroom theory and practical application for students worldwide.


